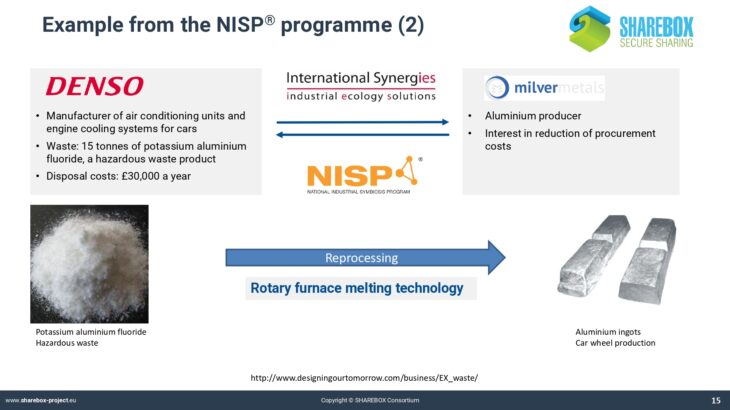
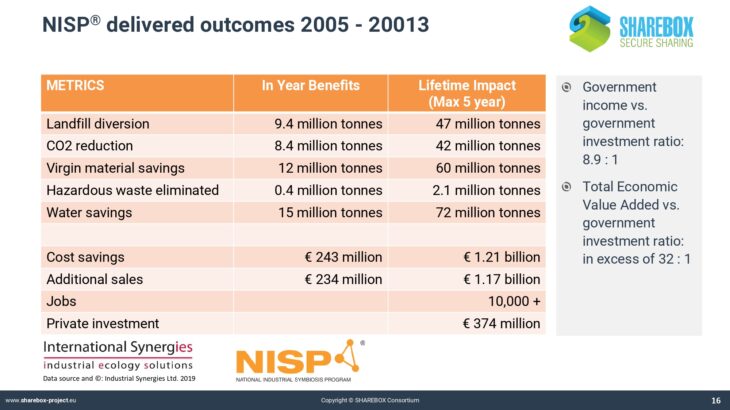
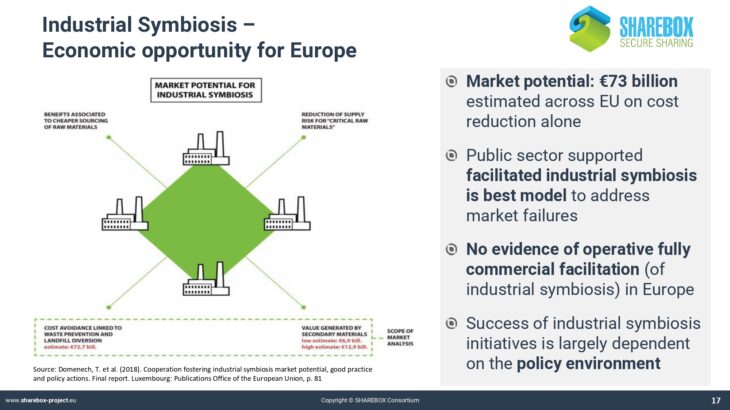
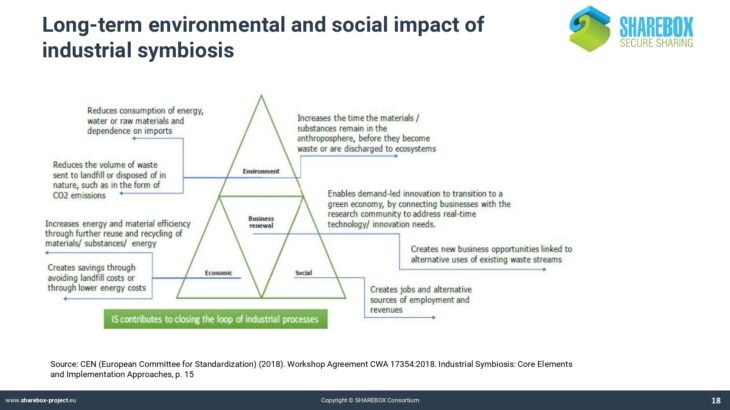
Welcome to SHAREBOX Training tool!!
With the interactive material available in this section you will be able to get:
- A solid understanding of the concept of Industrial Symbiosis, including economic benefits and cross-sectoral opportunities.
- Knowledge about SHAREBOX and its functionalities that support identification and evaluation of synergy opportunities and the process of creating synergies.
- Tips to handle the SHAREBOX software in an effective way.
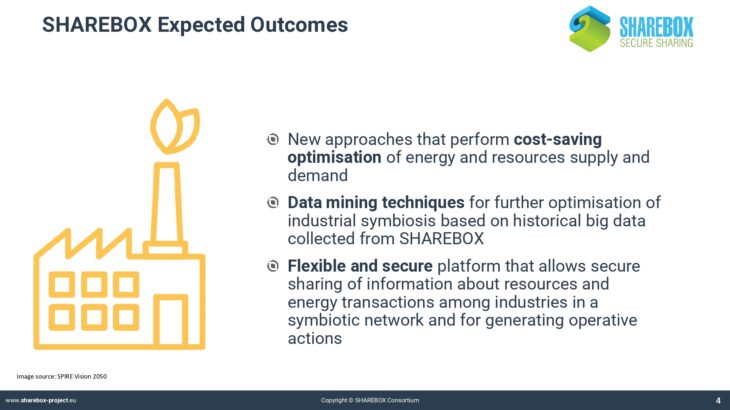
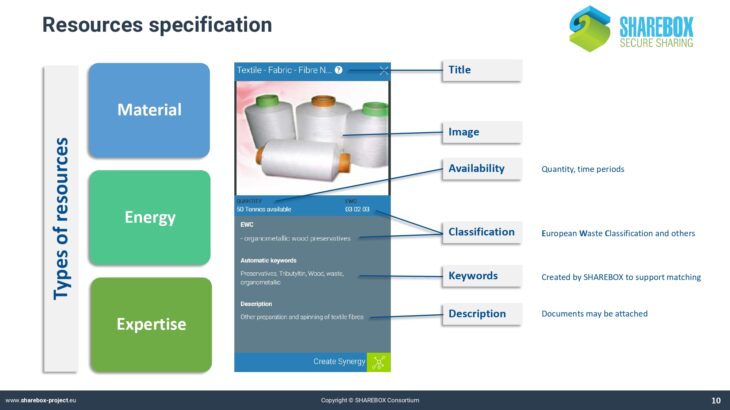
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
Agent Based Modelling
Agent-based modeling (ABM) is a methodology allowing to study complex systems consisting of autonomous decision-making entities. Each entity is modeled as an independent agent, which is provided with a set of goals it has to accomplish through the interaction with other agents and a set of rules of interaction.
The ABM approach is used to represent the individual stakeholders, their roles and interests in the IS design, and to simulate the business interactions among them, aimed at generating a generally acceptable (set of) solution(s) on how to implement the IS practice (e.g., which IS relationships to implement, how to share economic benefits arising from the cooperation, with which specific partners to cooperate), incorporated in a decision-support tool.

Energy Monitor

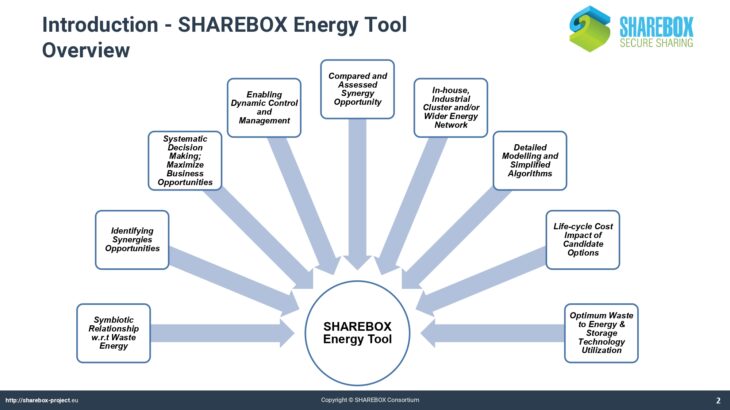
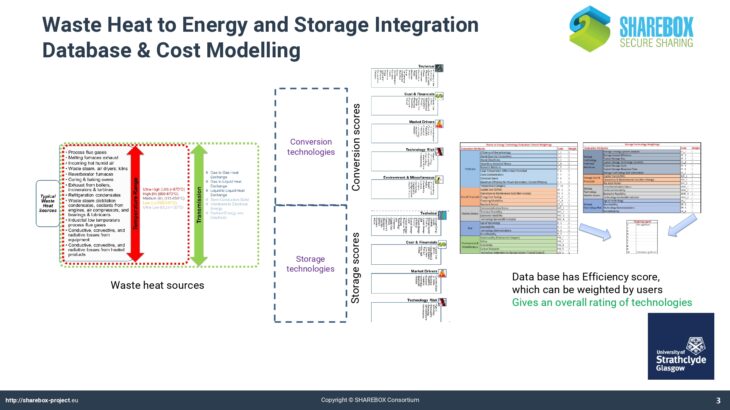
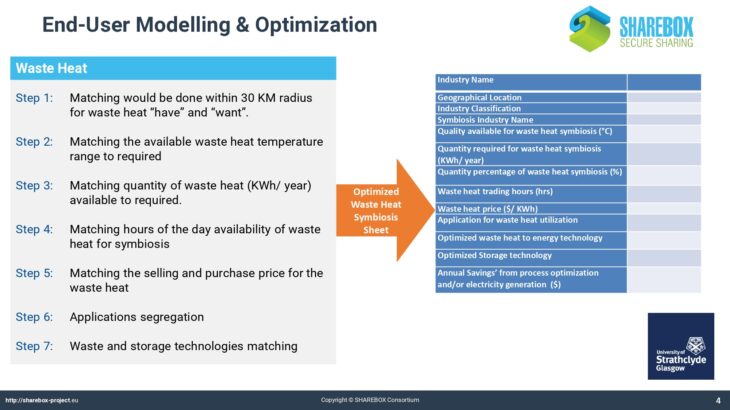
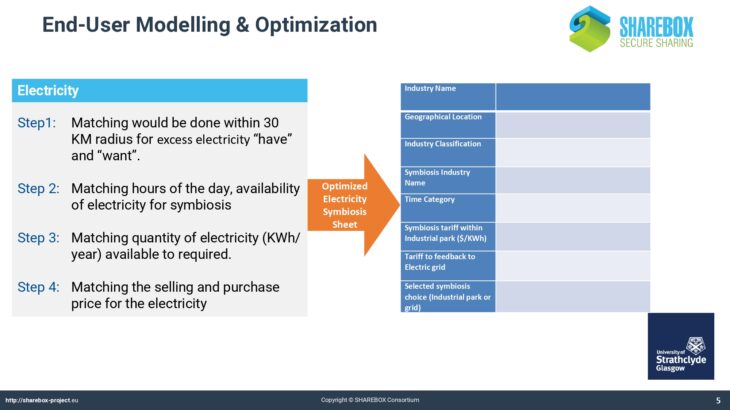
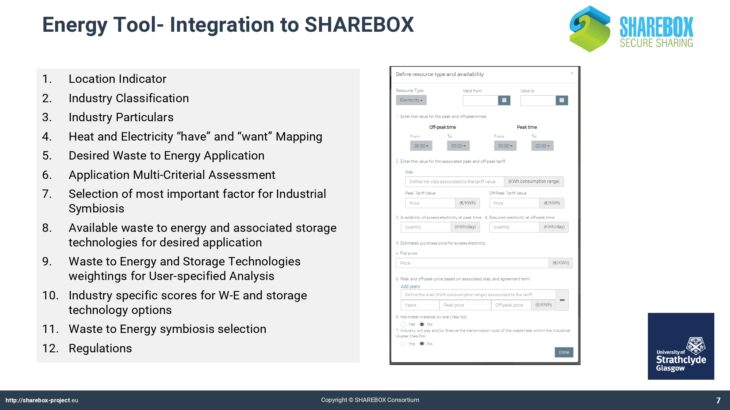
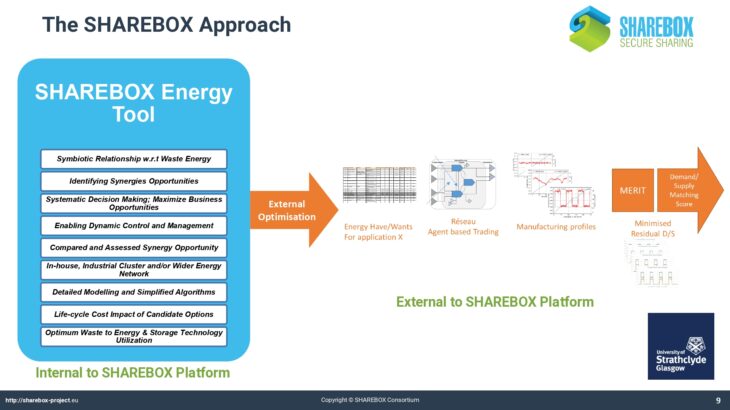
The Energy Tool allows users of SHAREBOX to establish and rank options for the recovery and use of energy bearing waste such as hot flu gases. It provides a list of compatible conversion or reuse technologies with likely performance and costs and indicates the appropriate scale of installations thereby facilitating collaboration between users with similar waste streams and hence the potential to trade.
The Energy Tool also allows users to analyse and establish optimum solutions for a region, that could take the form of an industrial park, based on the range of waste energy streams available within it. As such it will identify and quantify viable options for investment in energy conversion technologies for advanced SHAREBOX users such as Park Managers or Energy Service Companies
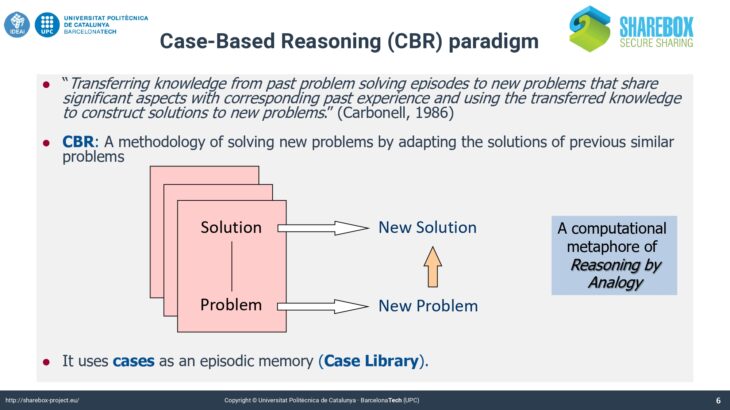
Case-Based Reasoning
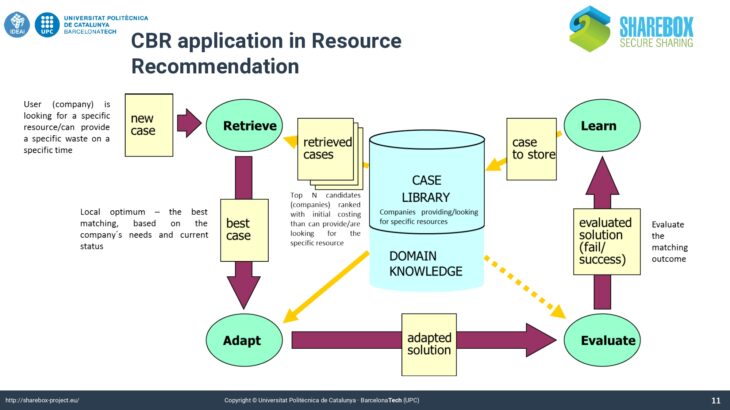
This paradigm of Artificial Intelligence aims to solve complex problems by reusing the accumulated experience in a concrete domain. This approach solves new problems in a domain reusing the previous solution given in the past to similar problems in the same domain (analogical reasoning). Thus, the solved problems constitute the “knowledge” about the domain. As more experienced is the system better performance achieves, because the experiences (cases or solved problems) are stored in the Case Base. This way the system is continuously learning to solve new problems.
This approach is known as Case-Based Reasoning (CBR). It is based on the theory of dynamic memory of Roger Schank, which states that the human memory is dynamic and change with its experiences along their lives. The main reasoning cycle in Case-Based Reasoning is depicted in the figure. There are four main tasks: retrieve similar cases to the new one to be solved; adapt the solution of the most similar case/s to fit the exact description of the new case; evaluate the performance of the solution proposed by the system; and finally, learn a new case from the new solved problem to enhance the experiential knowledge of the system.

Data Management

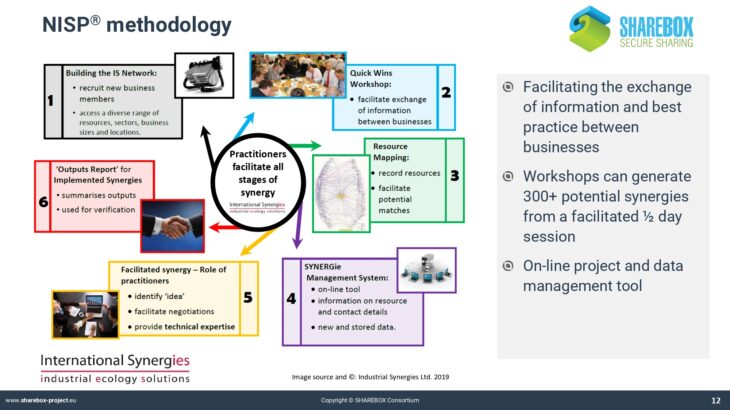
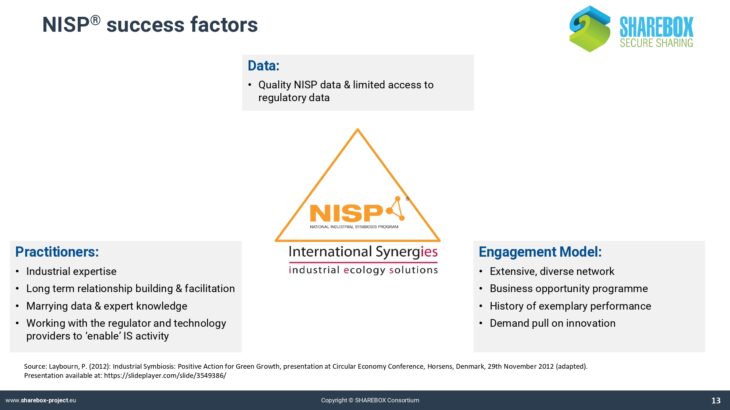
Current passive waste exchanges are often ‘e-bay style’ tools listing available resources, but lacking user support to identify reuse opportunities, or overcome information barriers to the reuse of complex industrial wastes. SHAREBOX builds on an existing commercial web-based resource reuse database SYNERGie®, currently hosting data from over 30,000 companies in 22 countries around the world, delivering business benefits by enabling identification and advancement of resource reuse opportunities.
SYNERGie® offers database, project management, and reporting functionality. SHAREBOX adds to this capability with decision support tools and modules enabling application of energy and filtration technologies.
PRESENTATION 1.
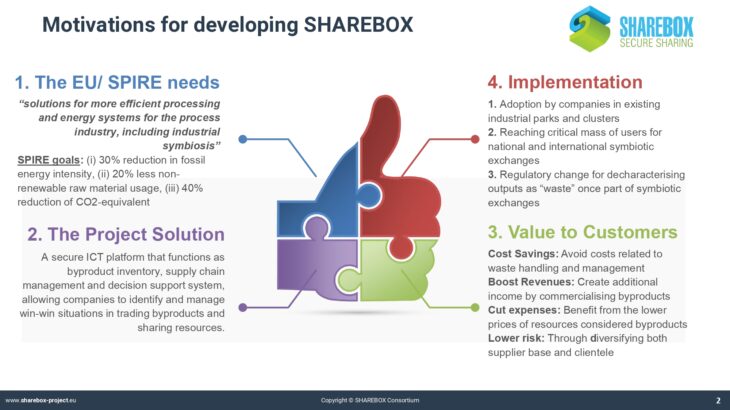
Industrial Symbiosis and its Benefits
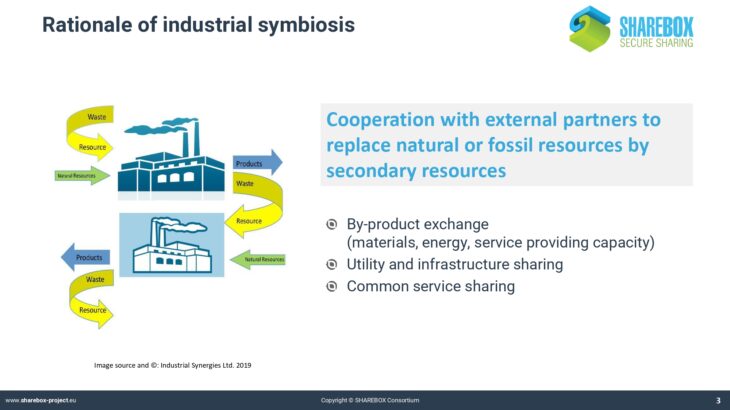
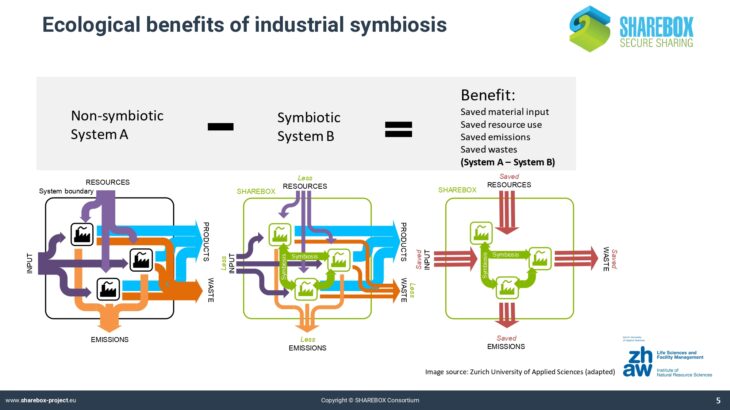
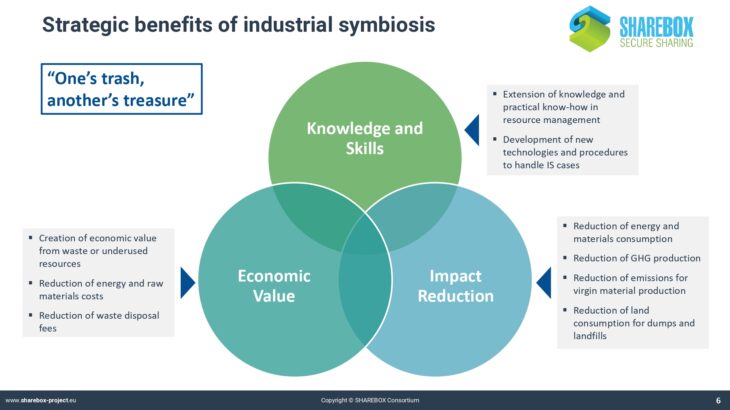
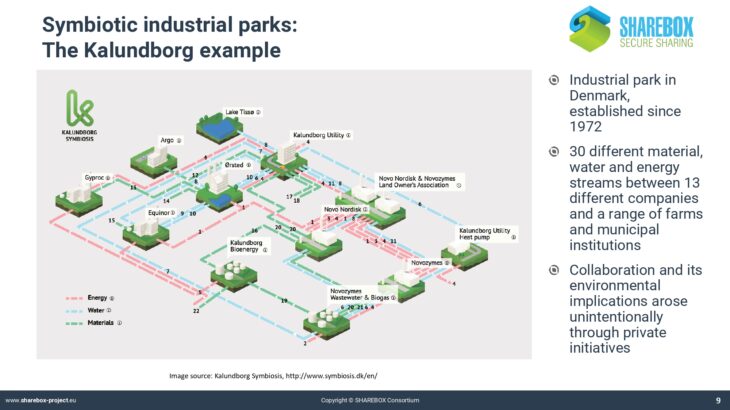
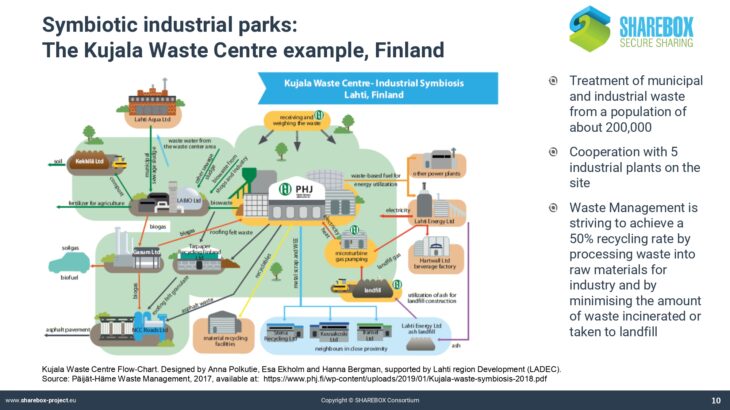
Whereas many companies are aware of the concept of circular economy and go to great lengths to reduce energy and material consumption in their internal processes, much less effort is spent on the creation of synergies beyond the organizational limits of an industrial production site.
Industrial parks in the chemical and process industry often only valorise a limited number of the most important downstream products by passing them on to other companies in a connected system.
Less attention is being paid to resources that only appear in smaller amounts or that could be valorised in synergies between partners across sectoral borders. In the companies, there is little to no knowledge about the potential value of such synergies.
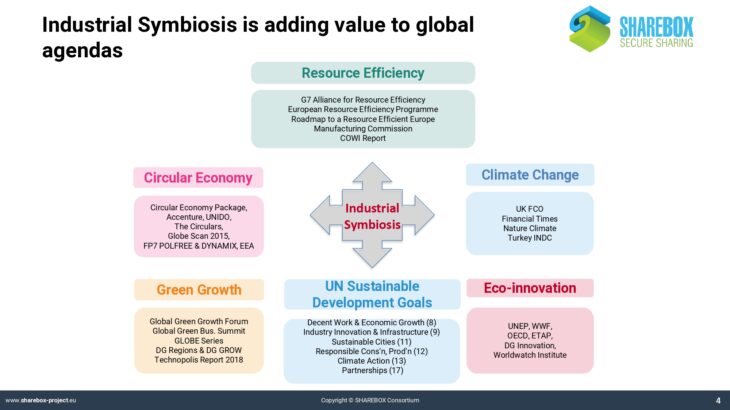
The presentation provides a definition of industrial symbiosis, explains the rationale of this concept and its importance for sustainable industrial development and competitiveness. It explains different approaches of industrial symbiosis and gives various examples in the form of case studies. It discusses barriers and success factors for implementation, and it introduces into the contents of the CEN Workshop Agreement on industrial symbiosis, which can be seen as the first step towards standardisation of IS-related procedures. Finally, the presentation informs future industrial applicants about which challenges they may have to expect and how to cope with them.
PRESENTATION 2.
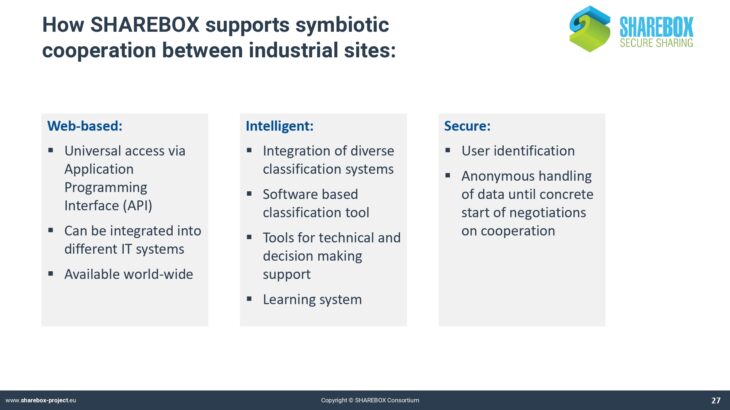
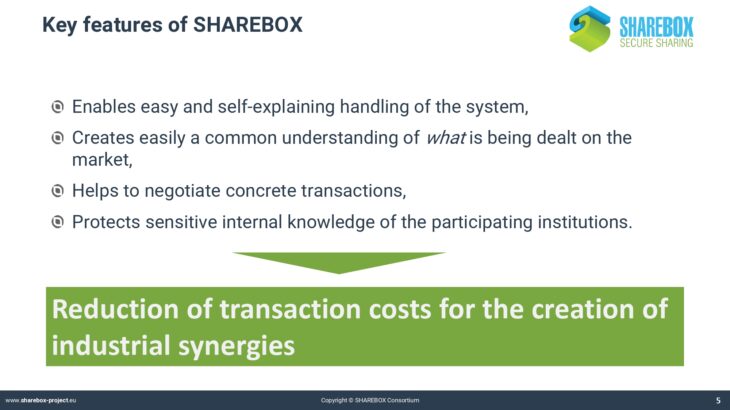
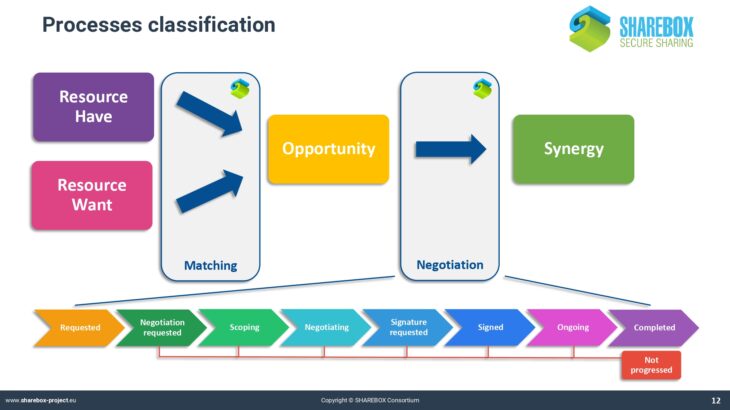
Basic functionalities of SHAREBOX
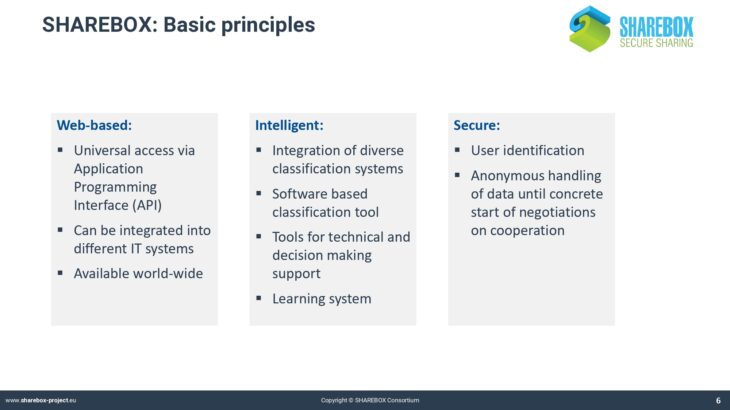
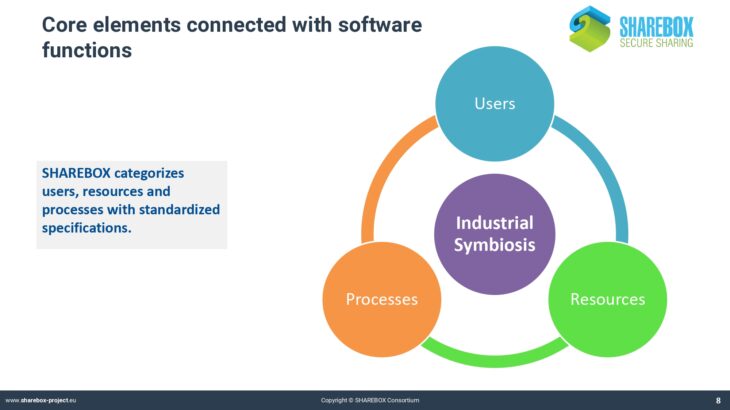
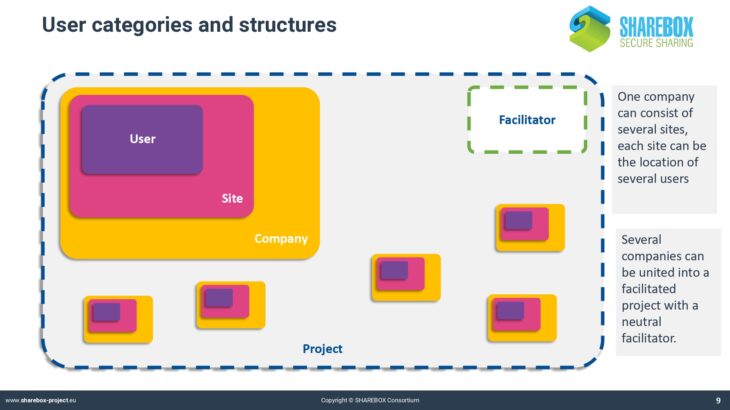
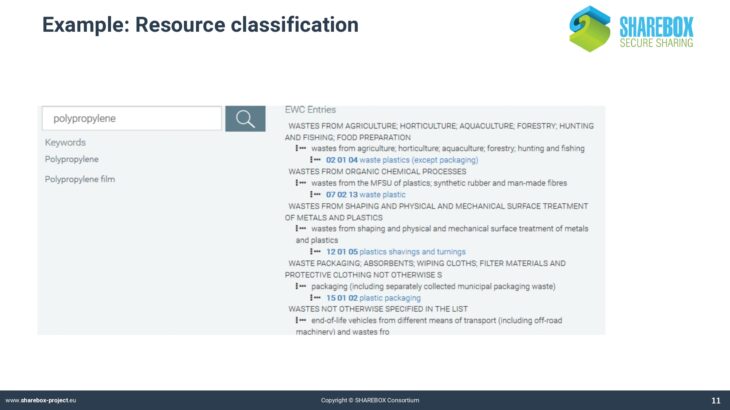
SHAREBOX has developed into a very powerful but also complex instrument. The platform uses aspecific syntax that may not be known from other computer applications. This applies for instance to the classification of industries and resources.
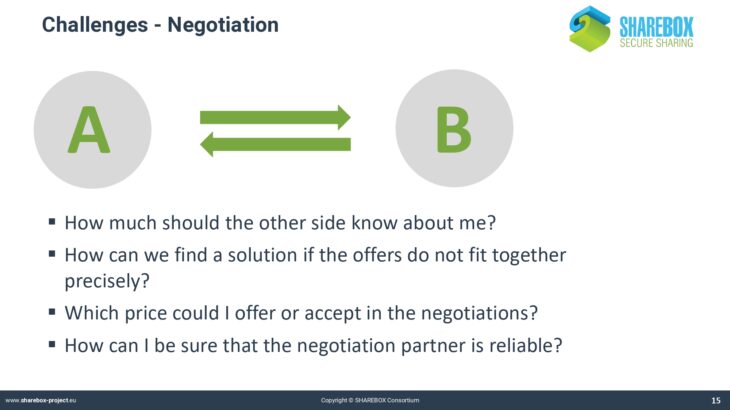
Traditional classification systems like NACE or EWC do not cover the whole range of possible cases that are applicable for SHAREBOX. The process of negotiating a synergy also requires a specific syntax that defines the objects and the steps of negotiation.
The presentation introduces into the motivation for creating the SHAREBOX web-based platform and how the objectives were met by the design of the platform.
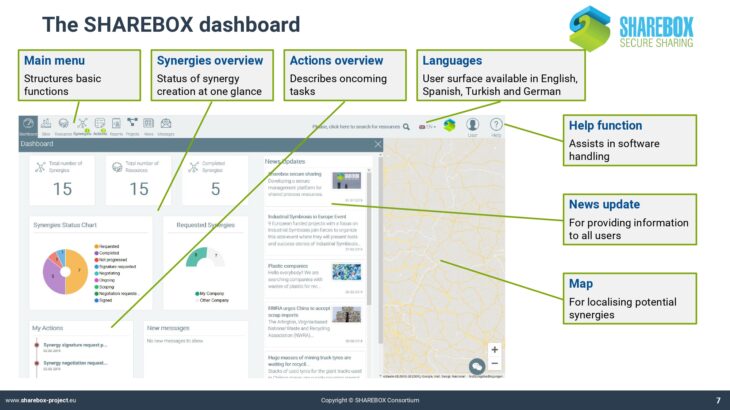
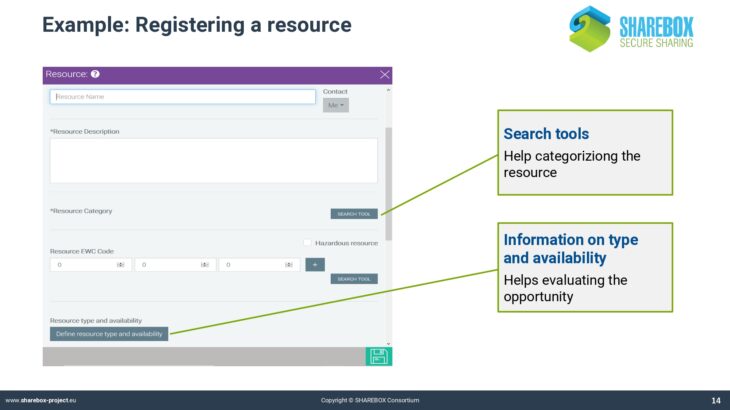
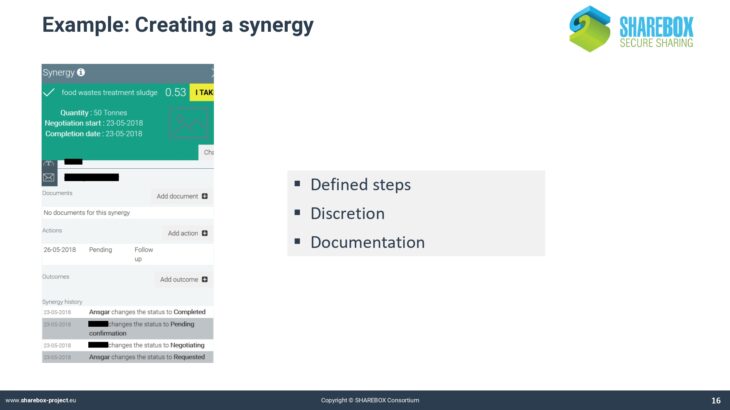
It explains the concept and the basic elements of the platform, using several screenshots.
It further introduces into the platform’s decision support tools.
PRESENTATION 3.
Evaluating IS and Cost Allocation
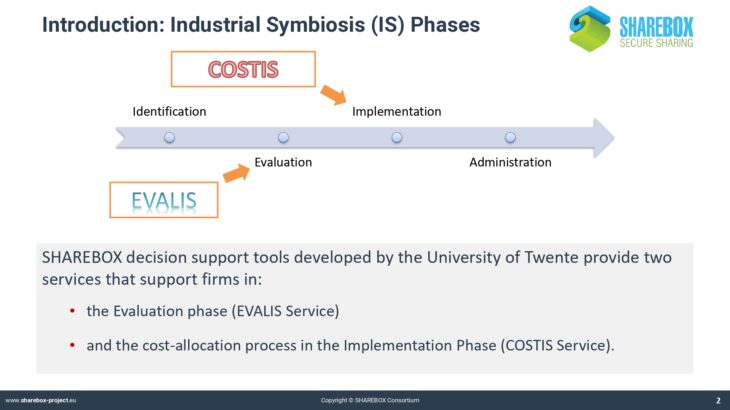
Several sophisticated decision support tools like the COSTIS and EVALIS recommender systems developed by University of Twente are integrated in SHAREBOX platform and require specific knowledge on their methodology and function.
The software already has an extensive help function, which presents the theoretical objective of the recommender systems and gives SHAREBOX user tips on how to use the tool to achieve better results.
The presentation introduces into the evaluation tools EVALIS and COSTIS.
It explains the difference between single and shared mode of these tools, and it provides instructions how to use them.
PRESENTATION 4.
How AI can support end-users evaluating IS potential
The application of Artificial Intelligence techniques to Industrial Symbiosis is currently a hot research topic.
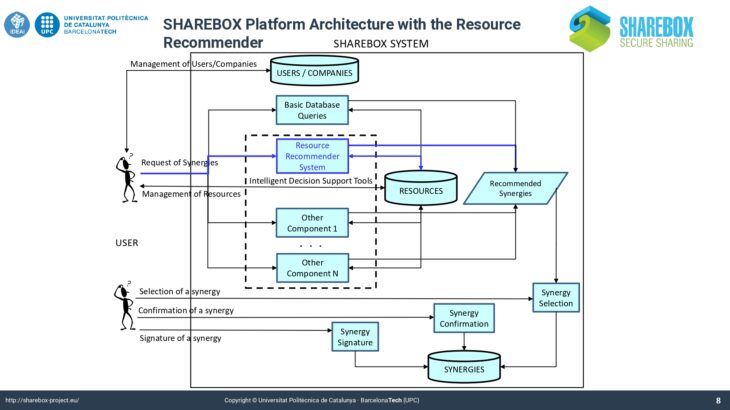
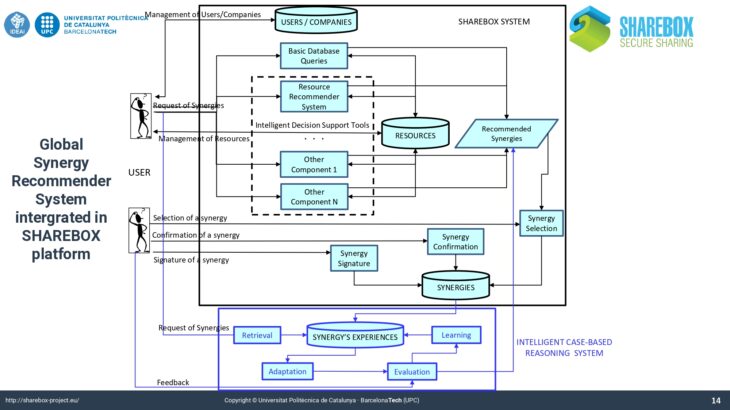
Two sophisticated recommenders like the Local Resource Recommender and the Global Synergie Recommender developed by Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya are integrated in SHAREBOX platform.
The presentation defines the basic terminology and discusses how artificial intelligence tools like recommender systems and case based reasoning can support the process of creating IS synergies. It describes the approach chosen in SHAREBOX, with the creation of a hybrid recommender system using case-based reasoning and ontological knowledge from European Waste Classifications to improve strategies for resource selection and starting of synergies. It further describes the key features for entering a resource and posting a user query. Examples from the SHAREBOX testing reports are given to explain the system’s functionality.
PRESENTATION 5.
Water treatment and filtering technologies in the context of industrial symbiosis
Industrial water consumption makes up 22% of global water use and up to half of the water use in North America and Europe.
The largest industrial consumers of water are thermal power, iron and steel, paper production, textiles, and petrochemical industry for different purposes as cooling water, process water, aggregate washing, concrete making, soil compaction or dust control. Industrial water reuse may help reduce water stress rates (ratio between water consumption and water reproduction), which are high to severe in many European countries.
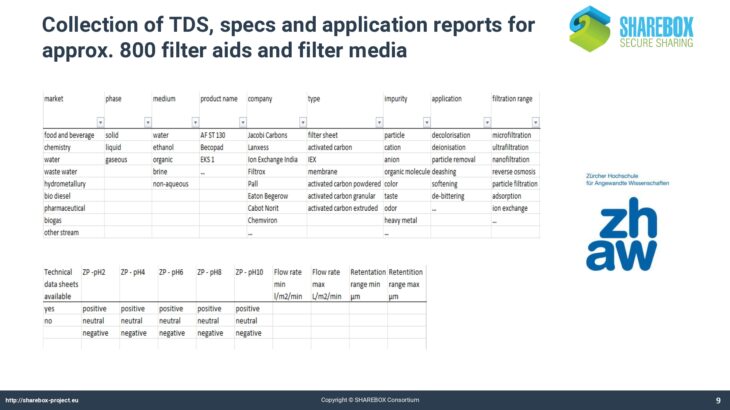
A filtering self-sustaining data based has been created in SHAREBOX project and technical consultancy services are offered through the platform to facilitate wastewater and other liquid waste resources synergies.
The presentations shows how SHAREBOX tackles the challenges that come along with creating waste or surplus water synergies by establishing a self-sustaining database for tailored purification and waste treatment technologies.
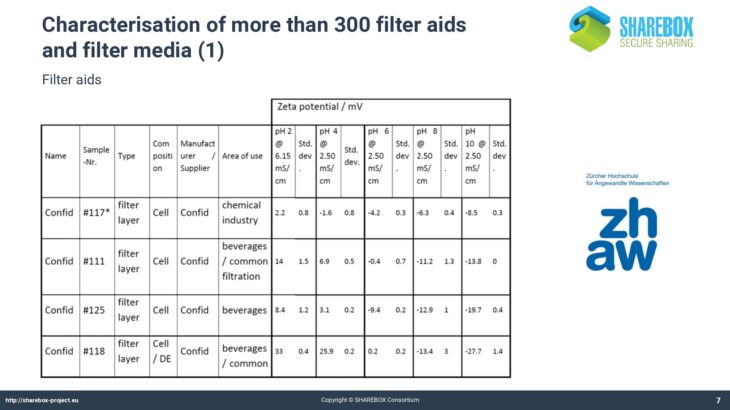
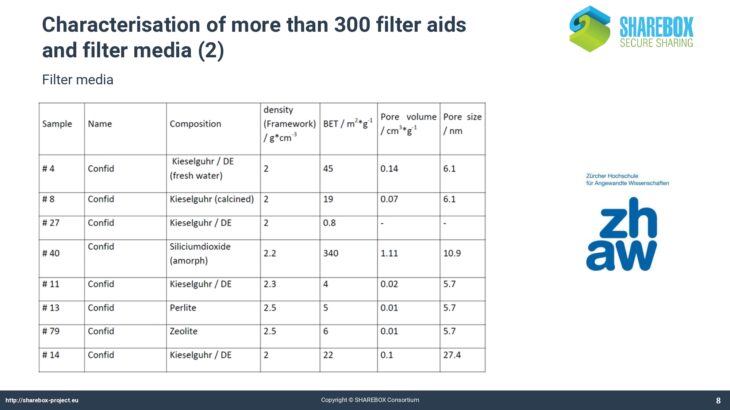
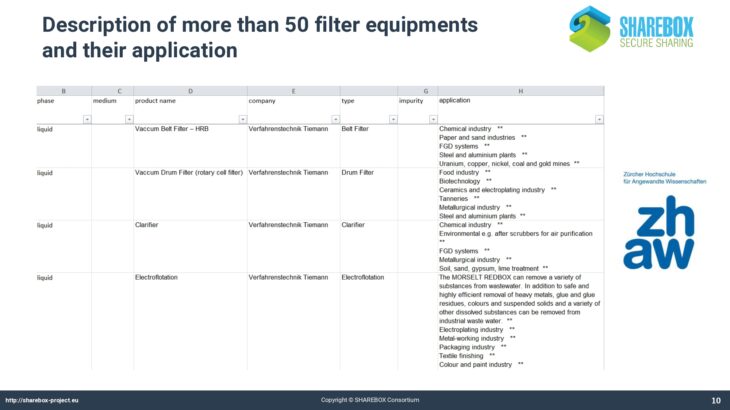
More than 300 filter aids and filter media and more than 50 filter equipment and their application have been characterized.
This together with the character of SX as a safe and discrete resource exchange platform provides valuable support to overcome the barriers of synergy implementation.
PRESENTATION 6.
Symbiotic exchange of energy: Technologies and management
In 2013, the industrial sector accounted for 25.1% of the total final energy consumption in the EU-287. The energy in industry is mostly used for process heating and cooling, which represents about 63% of the total industry final energy demand. In all these processes there is a portion of residual energy, as heat or cold waste, that escapes the system.
The waste heat from processes can be recovered and used in situ for direct heating purposes, electricity generation or heat pumps.
However, in Europe, due to different technical and non-technical barriers (financial, organizational, informational), the potential offered by energy waste reuse and recovery is largely untapped.
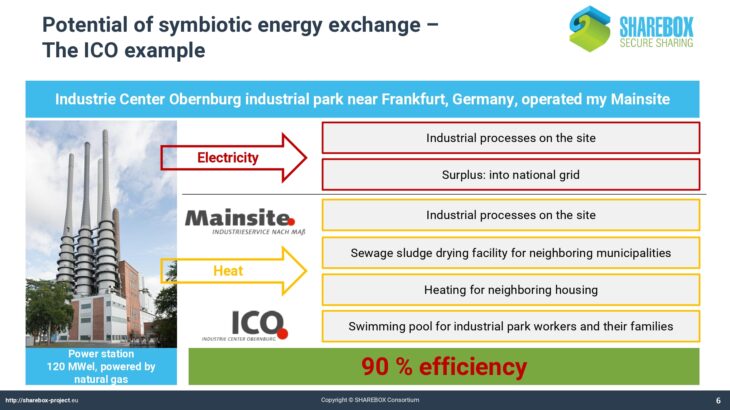
The presentation gives an example for synergetic use of electricity and waste heat in a German industrial park. It describes the challenges for successful implementation of energy-related synergies. The approach and various tools for waste energy management developed in the framework of the SHAREBOX project are explained.
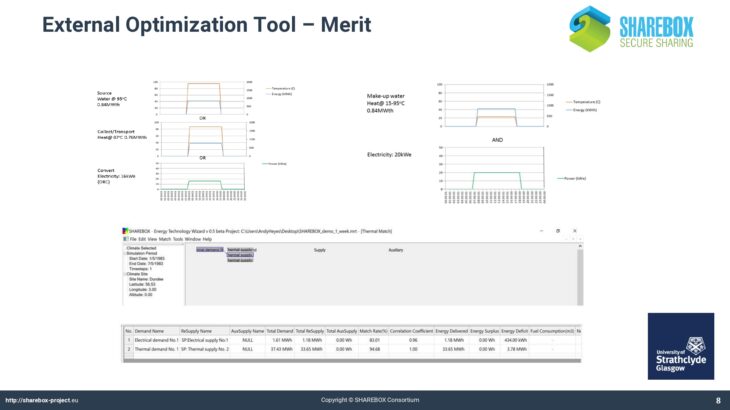
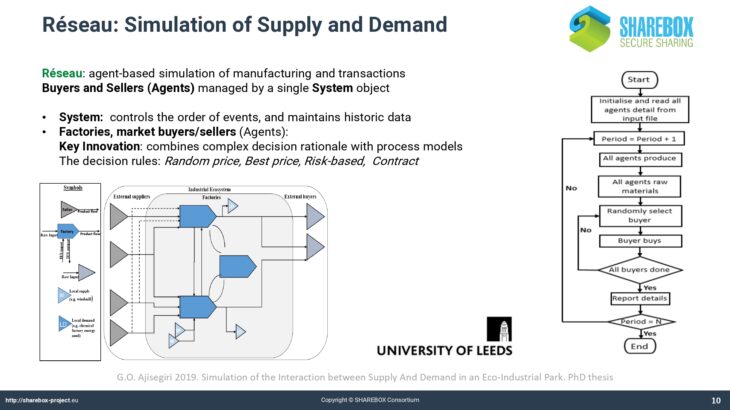
The “Reseau” tool developed by the University of Leeds supports waste energy management by an agent-based simulation of manufacturing and transactions. This tool will be made available on a public-domain basis.