Led by an ever-increasing pace of information technologies-driven transformations, industries are forced to continuously adapt and reinvent themselves and their processes to remain competitive. This recent raise of digital transformation of the industrial sector is more and more referred to as the Industry 4.0. This term refers to the fourth industrial revolution based on cyber-physical production systems (CPPS), the first three being the mechanisation of production via water and steam power (late 18thc.), the introduction of mass production using electrical power (early 20th c.) and the automation of production thanks to electronics and IT (1970s).
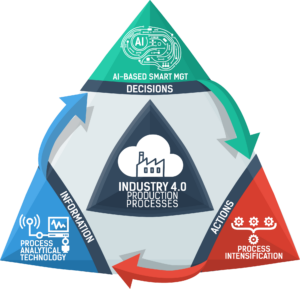
In an article published in 2015, BCG identifies nine pillars of the Industry 4.0: big data and analytics, autonomous robots, simulation, horizontal and vertical system integration, industrial Internet of Things, cybersecurity, cloud-based operations, additive manufacturing and augmented reality. A simpler way to look at the industry 4.0 production processes is illustrated in the figure above in which one considers the need of information to take the right decisions that are converted into a series of actions.
-
Information is provided by CPPSs, including process analytical technologies (PAT) and sensors, which enable plants to rapidly react to faults or market changes allowing autonomous organisation of production and maintenance management.
-
Decisions are based on artificial-intelligence smart management following the concept of horizontal integration. Technologies allows customised solutions, flexibility and cost savings in industrial processes which are also obtained by the constitution of global value chain networks. Internal company services or chains of companies constituting these networks share their data for more transparency of the operations enabling more flexibility andfast response to changes.
-
Eventually, industrials can take serious production transformation actions by optimising the processes of their production lines.
Governmental bodies have understood the importance of the Industry 4.0 and are promoting the adoption of its characteristics by companies. For instance, currently the SPIRE association is funding three projects led by IRIS Advanced Engineering. ProPAT aims to develop novel sensors and analysers and integrate them into a versatile global control platform for data acquisition, data processing and mining. SHAREBOX will provide robust and reliable in-real time information to effectively and confidently share resources (plant, energy, water, residues and recycled materials) with other companies in an optimum symbiotic ecosystem.IbD will create a holistic platform for facilitating process intensification design and optimization in processes in which solids are an intrinsic part.
Industry 4.0 is expected to have a tremendous impact on productivity, revenue growth, employment and investment. Are you willing to convert your company or to keep following the 20th-century paradigm? Then stay tuned to the development of ProPAT, SHAREBOX and IbD!

No Comments
Comments are closed.